Dogs, like humans, are susceptible to a variety of diseases that can affect their quality of life and longevity. As responsible pet owners, understanding these common ailments, their causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial for ensuring our furry friends lead healthy and happy lives. This article will delve into some of the most common diseases in dogs, exploring their causes, symptoms, and the best treatment options available.
Overview of Common Dog Diseases
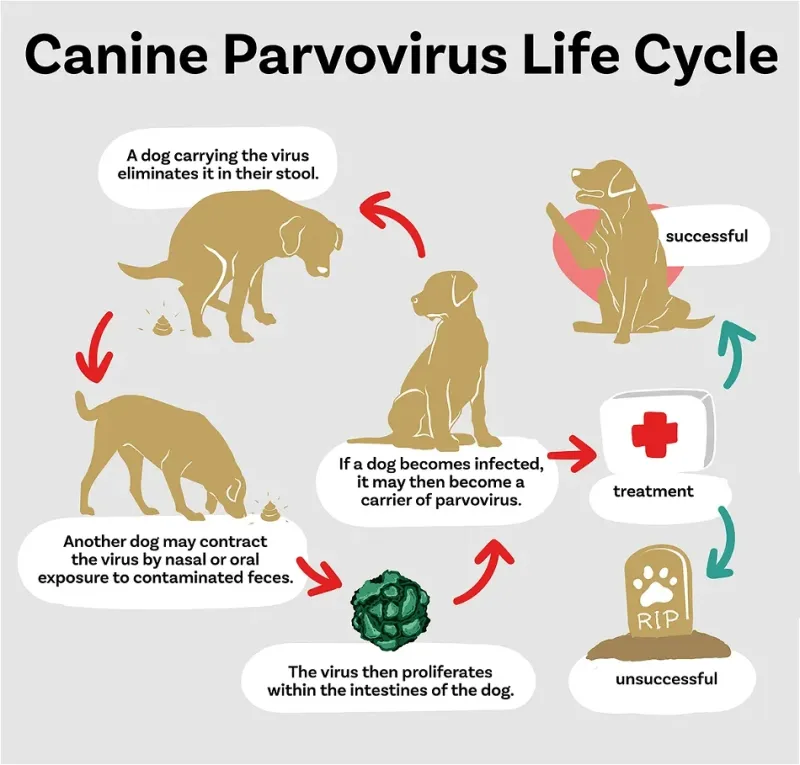
Canine Parvovirus, often referred to as Parvo, is a highly contagious viral illness that primarily affects puppies but can also strike adult dogs. The disease attacks the gastrointestinal tract, causing severe vomiting, diarrhea, and dehydration, and can be fatal if not treated promptly. Another common illness is Kennel Cough, a respiratory infection that spreads rapidly among dogs, especially in environments where they are in close contact, such as kennels and dog parks. This condition is marked by a persistent, forceful cough and can lead to more serious respiratory complications if left untreated.
Heartworm disease is another severe condition caused by parasitic worms living in the heart and lungs of affected dogs. Transmitted through mosquito bites, this disease can be life-threatening, leading to heart failure and lung disease. Lyme disease, transmitted by ticks, is prevalent in certain regions and can cause fever, lameness, and swollen joints in dogs. Canine distemper, a viral disease affecting multiple body systems, is also highly contagious and can be fatal, with symptoms ranging from fever and nasal discharge to seizures and paralysis.
Ear infections are a frequent issue in dogs, often caused by bacteria or yeast. They can lead to discomfort and severe complications if not treated promptly. Additionally, skin allergies are common in dogs, caused by various allergens such as pollen, food, or flea bites, resulting in itching, redness, and hair loss.
Causes of Common Dog Diseases
Understanding the causes of these diseases is essential for prevention and early detection. Viruses and bacteria are primary culprits in many canine diseases. Canine Parvovirus and distemper are viral infections that spread through contact with infected animals or their secretions. Bacterial infections, such as those causing kennel cough and ear infections, often spread in environments where many dogs congregate.
Parasites like heartworms and ticks also pose significant health risks to dogs. Heartworm disease is spread through mosquito bites, while ticks transmit Lyme disease. Both parasites can cause severe and sometimes fatal conditions if not addressed.
Environmental factors play a crucial role in the prevalence of diseases like Lyme disease, which is more common in areas with high tick populations. Skin allergies often result from environmental allergens, making it essential to manage a dog’s surroundings to minimize exposure.

Genetics and breed predisposition also contribute to disease susceptibility. Some breeds are more prone to certain conditions due to their genetic makeup. For instance, large breeds are more susceptible to hip dysplasia and heart disease, while breeds with floppy ears are more prone to ear infections.
Symptoms of Common Dog Diseases
Recognizing the symptoms of these diseases is key to seeking timely veterinary care. Canine Parvovirus typically presents with severe vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, and loss of appetite. The rapid progression of symptoms underscores the need for immediate veterinary attention.
Kennel cough is characterized by a persistent, forceful cough, often accompanied by sneezing and nasal discharge. The incubation period can vary, making it challenging to identify the source of infection immediately.
Heartworm disease symptoms include coughing, fatigue, weight loss, and difficulty breathing. In advanced stages, heart failure and other severe complications can occur, emphasizing the importance of regular heartworm prevention and testing.
Lyme disease symptoms, such as fever, lameness, swollen joints, and loss of appetite, often appear weeks after a tick bite. Early treatment is crucial to prevent long-term damage.
Canine distemper initially causes fever, nasal discharge, and eye inflammation, progressing to neurological symptoms like seizures and paralysis. Early detection and supportive care are vital to improve outcomes.
Ear infections often lead to symptoms like ear scratching, head shaking, discharge, and a foul odor. Redness and swelling inside the ear are also common indicators.
Skin allergies manifest as itching, redness, swelling, and hair loss. Persistent scratching can lead to secondary infections, requiring prompt treatment to alleviate discomfort.
Treatments for Common Dog Diseases
Effective treatment varies depending on the disease but generally involves a combination of medication, supportive care, and lifestyle changes. For Canine Parvovirus, treatment focuses on supportive care, including hydration, anti-nausea medications, and antibiotics to prevent secondary infections. Early veterinary intervention is crucial for survival.
Kennel cough is typically treated with antibiotics, cough suppressants, and rest. Isolating infected dogs helps prevent the spread of this contagious disease.
Heartworm disease treatment is complex and involves medications to kill the adult heartworms and larvae, along with possible surgical intervention in severe cases. The recovery process requires strict rest to avoid complications.
Lyme disease is treated with antibiotics, with early detection being key to preventing chronic issues. Regular tick prevention and checks are essential, especially in regions where Lyme disease is prevalent.

Canine distemper lacks a specific cure, so treatment focuses on supportive care, including fluids, anticonvulsants, and antibiotics for secondary infections. Long-term care may be necessary for dogs that recover but suffer from lasting neurological damage.
Ear infections are treated by cleaning the ear and applying topical medications. Antibiotics may be prescribed for bacterial infections. Regular ear maintenance helps prevent recurrence.
Skin allergies are managed with antihistamines, steroids, and topical treatments to relieve itching and inflammation. Identifying and avoiding allergens is crucial for long-term management.
Preventive Measures for Common Dog Diseases
Prevention is always better than cure, and several measures can help protect dogs from common diseases. Regular vaccinations are essential to prevent diseases like Parvo, distemper, and kennel cough. Adhering to vaccination schedules and booster shots ensures sustained immunity.
Routine veterinary check-ups are vital for early detection and prevention of diseases like heartworm and Lyme disease. These visits also provide an opportunity to discuss preventive care and address any health concerns promptly.

Parasite control is crucial, with regular use of flea, tick, and heartworm preventatives. Various products are available, including topical treatments, oral medications, and collars.
Maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise contributes significantly to a dog’s overall health. A balanced diet supports the immune system, while exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of various diseases.
Environmental management, such as reducing exposure to ticks and allergens, is essential for preventing diseases like Lyme disease and skin allergies. Keeping the living environment clean and free from potential hazards also minimizes the risk of infections.
In conclusion, understanding common diseases in dogs, their causes, symptoms, and treatments, is crucial for responsible pet ownership. Early detection and preventive measures can significantly improve a dog’s quality of life and longevity. Regular veterinary care, combined with a supportive home environment, can make a substantial difference in managing and preventing these diseases. If you suspect your dog is showing signs of illness, consult your veterinarian promptly and implement the preventive strategies outlined here to keep your furry friend healthy and happy.

After 5 years in a high pace business management role, I partnered with an e-commerce developer to start building Dog Supplies Warehouse.
Our number one goal is to make sure all products are managed and delivered to our customers door fast and accurately.
