Joint pain in dogs is a common yet often overlooked issue that can significantly impact a dog’s mobility, comfort, and overall quality of life. Just like humans, dogs can experience joint pain due to various factors such as aging, injury, or underlying medical conditions. As a responsible pet owner, it’s essential to recognize the signs of joint discomfort and take proactive steps to manage it effectively. Doing so not only improves your dog’s daily life but also helps extend their ability to enjoy activities without suffering from debilitating pain. This guide will dive deep into the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures that can help you provide the best care for your furry companion.

Understanding Joint Pain in Dogs
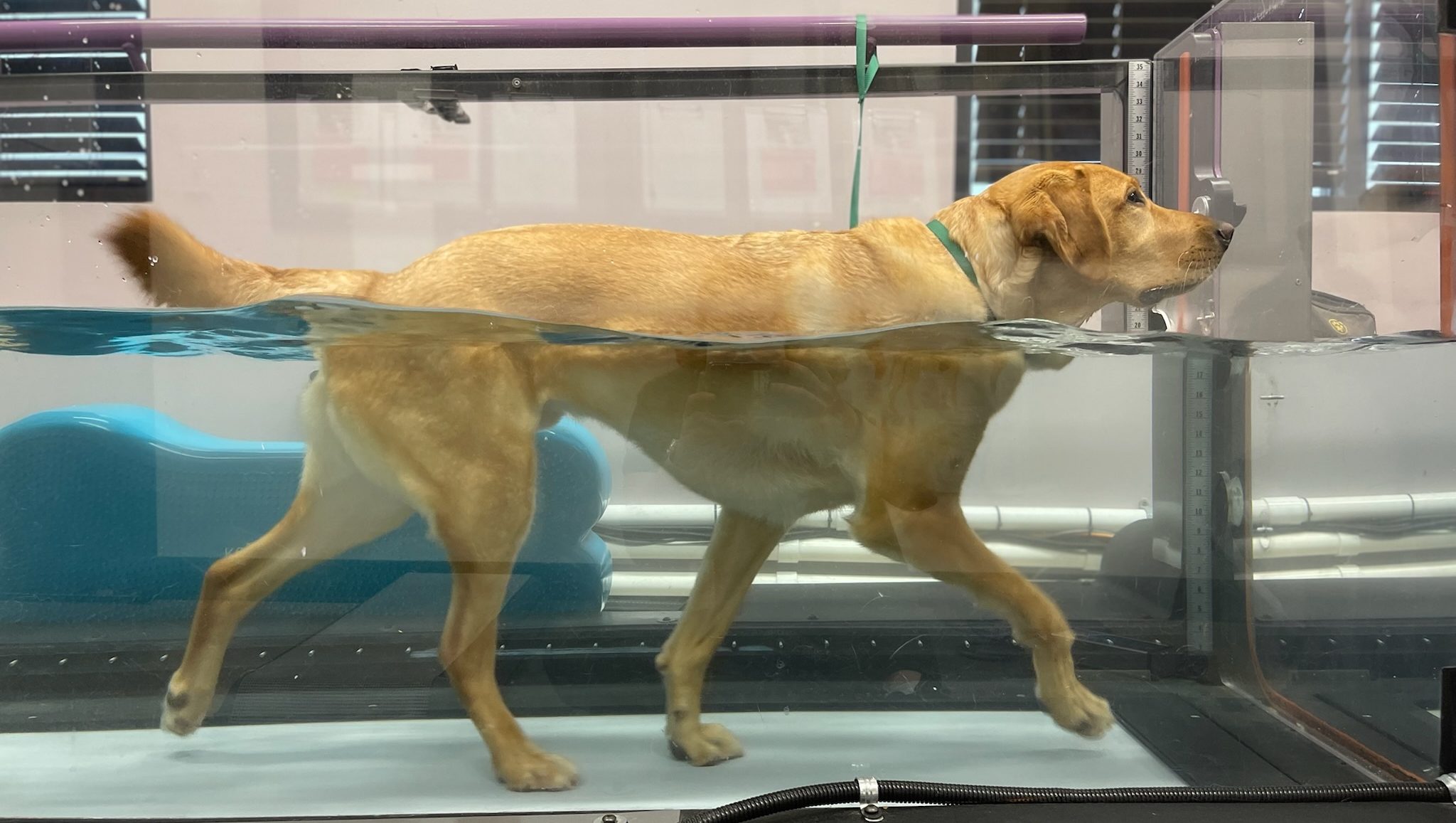
Joint pain in dogs, characterized by discomfort or inflammation in the joints, can range from mild to severe and often leads to restricted movement and a decrease in a dog’s overall well-being. Joint pain can be classified as either acute or chronic. Acute joint pain typically arises from sudden injuries like sprains or fractures, while chronic joint pain tends to develop slowly over time, often due to conditions like arthritis or degenerative joint diseases.
Recognizing the early symptoms of joint pain is crucial. Common signs include limping, stiffness, a reluctance to run, jump, or climb stairs, and noticeable changes in behavior such as increased irritability or depression. Dogs experiencing joint pain may also sleep more than usual, avoid physical activities they once enjoyed, and even exhibit a reduced appetite. Identifying these symptoms promptly can lead to quicker diagnosis and treatment, reducing the impact of joint pain on your dog’s quality of life.
Causes of Joint Pain in Dogs
There are several causes of joint pain in dogs, many of which are linked to the wear and tear on the body as dogs age, but some can occur at any life stage. The most common cause of chronic joint pain is arthritis, which is an inflammation of the joints. Osteoarthritis, the most prevalent type, involves the breakdown of cartilage that cushions the joints, leading to pain and stiffness as the bones rub against each other. Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune condition, can also lead to joint damage and discomfort.
Hip dysplasia, another major cause of joint pain, primarily affects large dog breeds such as German Shepherds, Labradors, and Golden Retrievers. This condition occurs when the hip joint doesn’t develop properly, leading to gradual degeneration and discomfort. In addition to genetic factors, injuries such as ligament tears, fractures, or sprains can lead to joint problems if not treated properly.
Other contributing factors include obesity, which places additional stress on the joints, and congenital abnormalities. Certain diseases like Lyme disease and immune-mediated diseases can also trigger joint pain. In puppies, rapid growth, particularly in large breeds, can contribute to joint issues as well. Understanding the underlying cause of your dog’s joint pain is key to determining the most effective treatment.
Diagnosing Joint Pain in Dogs
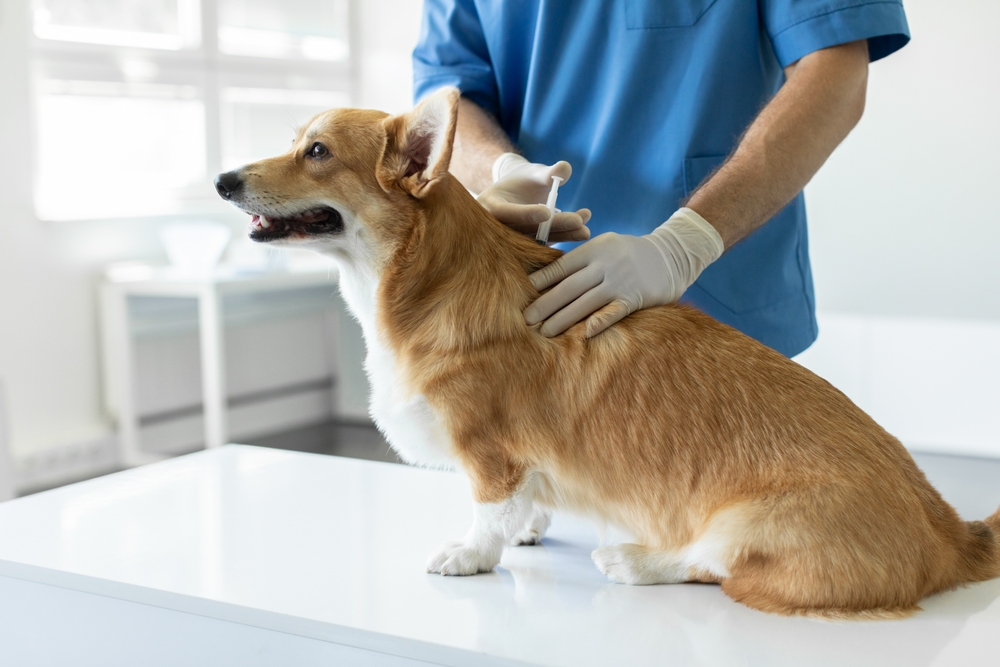
Proper diagnosis of joint pain is essential to ensure that your dog receives the right treatment. A visit to the veterinarian will typically begin with a thorough physical examination where the vet will check for signs of pain, swelling, or abnormalities in movement. During this examination, the vet may also review your dog’s medical history to identify any pre-existing conditions that could contribute to joint problems.
To gain a clearer picture of the condition, diagnostic tools such as X-rays and MRI scans are commonly used. These imaging techniques help pinpoint the severity of joint degeneration, fractures, or inflammation. In some cases, blood tests may be performed to rule out infections or autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. If a more detailed view is required, joint fluid analysis may be conducted to examine inflammation levels and detect infections or abnormalities. With a precise diagnosis, your veterinarian can recommend an appropriate treatment plan tailored to your dog’s specific needs.
Treatment Options for Joint Pain
Treating joint pain in dogs often involves a multi-faceted approach that combines medications, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies. Medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed to manage pain and reduce inflammation. In addition, supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin are widely used to support joint health by promoting cartilage repair and reducing stiffness.
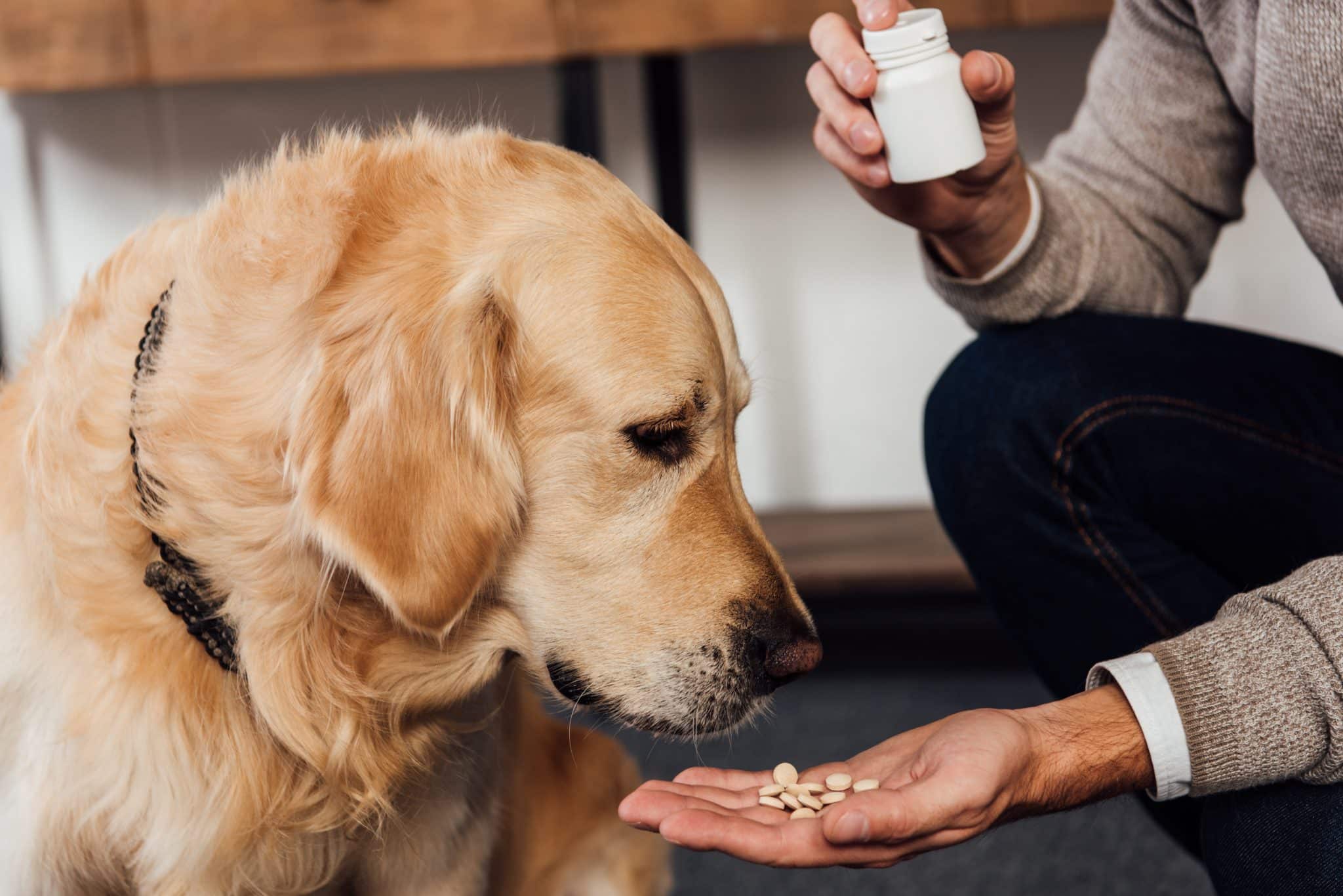

For dogs with more advanced joint issues, physical therapy can play a vital role in improving mobility. Techniques such as hydrotherapy, massage, and specific therapeutic exercises help build muscle strength and reduce pain. Hydrotherapy, in particular, is effective because the buoyancy of water reduces the stress on joints while allowing for more comfortable movement.
In severe cases where joint damage is extensive, surgical interventions like joint replacement or arthroscopy may be necessary to restore function and alleviate pain. Additionally, alternative therapies such as acupuncture, laser therapy, and chiropractic care have gained popularity in recent years for their potential to reduce pain and improve joint function. These holistic approaches can be valuable complements to conventional treatments, offering relief without the side effects of long-term medication use.
Managing Joint Pain at Home
In addition to veterinary care, there are several ways you can help manage your dog’s joint pain at home. Maintaining a healthy weight is one of the most important factors, as extra weight places unnecessary strain on your dog’s joints. Providing a well-balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and joint-supporting nutrients can help reduce inflammation and improve overall joint health.
Exercise is essential, but it’s important to strike a balance between keeping your dog active and avoiding overexertion. Low-impact activities such as swimming, gentle walks, and controlled play sessions are ideal for dogs with joint pain. Avoid activities that involve high-impact movements like jumping or running on hard surfaces.
Creating a comfortable living environment for your dog is another key aspect of home care. Investing in orthopedic dog beds, using ramps to help your dog avoid jumping, and installing non-slip mats on slippery floors can significantly reduce strain on their joints. Ensuring your dog has a quiet, comfortable space to rest can also aid in recovery and pain management.
Preventive Measures
Preventing joint pain in dogs starts with early detection and a proactive approach to their overall health. Regular veterinary check-ups allow for early diagnosis of joint issues, which can prevent conditions from worsening over time. For breeds predisposed to joint problems, responsible breeding practices and genetic screenings are crucial to minimizing the risk of inherited conditions like hip dysplasia.
Additionally, proper training during puppyhood can help reduce the risk of joint injuries later in life. Avoiding activities that involve excessive jumping or running, especially for large breeds, can help protect your dog’s joints. Ensuring a consistent exercise routine and managing your dog’s weight throughout their life are key components in preventing joint problems as they age.
Caring for a dog with joint pain requires attentiveness, compassion, and a commitment to providing both professional treatment and home care. By understanding the symptoms and causes of joint pain, obtaining an accurate diagnosis, exploring various treatment options, and implementing effective management strategies at home, you can significantly improve your dog’s quality of life. Regular veterinary care, combined with preventive measures such as maintaining a healthy weight and creating a comfortable home environment, can make all the difference. If you suspect your dog is experiencing joint pain, consult with your veterinarian and begin addressing the issue early. With proper care, your dog can lead a more active, pain-free life.

After 5 years in a high pace business management role, I partnered with an e-commerce developer to start building Dog Supplies Warehouse.
Our number one goal is to make sure all products are managed and delivered to our customers door fast and accurately.

![Dog taking medication]](https://dogsupplieswarehouse.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/Dog-taking-medication-1024x684.jpg)